Effects of Common Herbs used in Equine Supplements
This paper reviews literature related to Phytomedicine (Herbal medicine) using therapeutic plants, plant parts or plant-derived substances. Commonly used in supplements across the horse industry, including echinacea, valerian, garlic, ginger, ginseng, yucca, bee pollen, devil’s claw and more. Many plants may affect the immune system by increasing stressor resistance (Adaptogens) or activating nonspecific/innate infection defence mechanisms (immunostimulants), as well as an aid against different diseases, metabolism, and overall health.
Although they are largely unregulated, few studies have investigated safety and efficacy. It is naively assumed that they are safe 'natural' components. However, some contain prohibited substances such as: salicylates, heroin, cocaine, marijuana and steroids. In addition, there is a change of herbal toxicity, drug-like activities and possible interactions between medicines and herbs. For that reason, caution is required when implementing their use and essential for the health and well-being of horses.
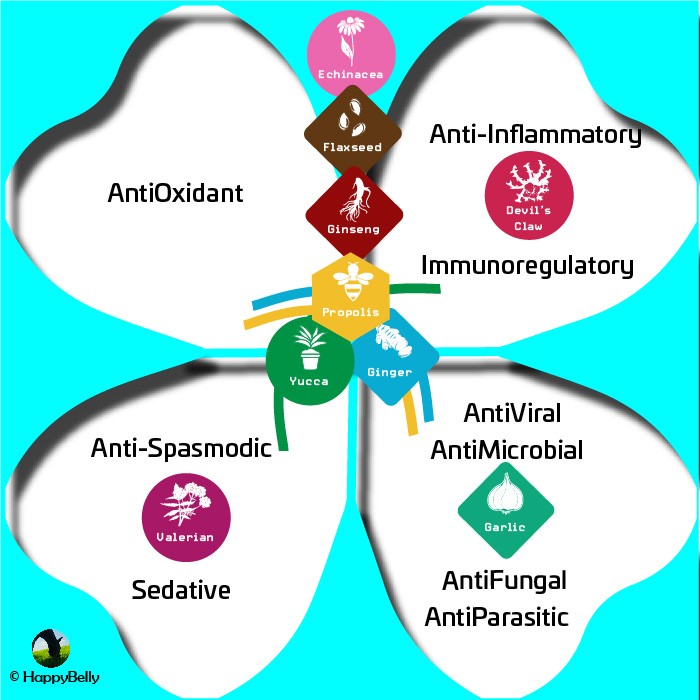
As illustrated according to Table 1 from the article, some plants are known to have multiple effects. Devil’s Claw has been found to mostly be anti-inflammatory and also regulate the immune system. Echinacea, Flaxseed and Ginseng have been found to serve as antioxidants.
Additionally, Garlic has been found to be very potent against viruses, microorganisms, fungi and parasites. Wheareas Propolis and Ginger combine these effects along with anti-inflammatory, immunoregulation and antioxidative actions. Finally, Valerian has been found as an effective anti-spasmodic and sedative agent, as well as Yucca which also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects. Thus, illustrating a wide range of effects, which should be functionally used with thoughtfulness and understanding.
Expert opinion by Shirley Ferber
Though more research is required, it is clear that the use of herbal medicine as harmless or inactive is a gross misconception. Whereas evidence shows some plants could be very active and even pose risk to health and welfare in unregulated doses or combinations. Remember, most modern western drugs and treatments were derived from natural sources and later synthesized or further developed. Thus, when choosing an equine supplement, it is essential to check if the manufacturer has regarded the effects and purpose of added functional herbs.
> From: Williams et al., The Veterinary Journal 178 (2008) 21-31. All rights reserved to ©Elsevier 2008. Click here for the online summary.