
Diet and nutrient intakes among elite show jumpers
This study into feed and nutrient intake among elite show jumpers was conducted during a 4-day international competition with events between 1.5- and 1.6 meter. A total of 34 horses were evaluated representing eight countries, including: 30 warmblood breeds (Dutch Warmbloods, Zangersheide, Belgium Warmbloods).
Feed intake averaged 11 kg hay and 4 kg grain, approximately 2.8% of body weight. The digestible energy being fed was close to the National Research Council (Nutrient Requirements, 2007) for a horse at “heavy” or “very heavy” work (see table below). The majority was fed an electrolyte supplement, received oral joint supplements (or injections) and used ulcer medications.
Crude protein in the offered diet averaged 1,055 g per day (2 g/kg body weight), which is similar to requirements for a horse in heavy work. Calcium in the diet met 205% of the NRC requirements. The dietary phosphorus in the diet met only 87% NRC requirements. However, no deficiency symptoms were noted and therefore the NRC requirement may be too high.
Almost all horses were offered timothy grass hay that was locally sourced by the facility. An analysis of the hay reported it was relatively low in protein and phosphorus. This could have been a problem if it was offered for a longer period of time. Due to travel constraints, it is common to arrive at show facilities without bringing own hay or feed. Horse owners should request hay analyses whenever hay is provided. Results should be discussed with the horse’s nutritionist.
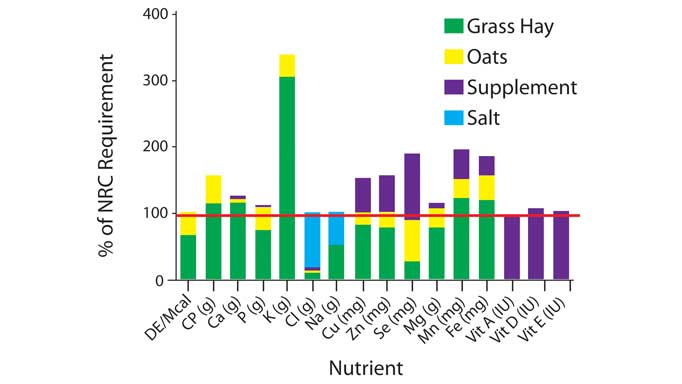
NRC nutritional requirements for a horse (500 kg) in heavy work
> S.E. Pratt-Phillips / Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 43 (2016) 39–43. All rights reserved to Elsevier Inc. Click here for the J-EVS summary


